- Details
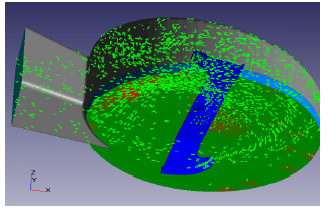
In this paper, the modeling and simulation of the blood flow in the real patient heart is described. In order to cure the patients with cardio vascular disorder it is important to make appropriate choice of an artificial heart valve, it is important to exactly understand the behavior of the heart blood flow of the specific patient under treatment. The presented approach is based on the Magnetic Resonance Imaging/Tomography, which provides the necessary input to create the heart shape (“its geometry”) and its variation in time (tens or hundreds of frames) to define the internal time-dependent heart volumes for one heartbeat. Once this geometry is defined, the CFD software is applied to simulate the internal blood flow and further on visualize it to enable its further analysis. The applied CFD tool is FlowVision, due to its possibility to fully automatically perform the mesh generation of arbitrary shapes, as the heart geometry requires. In addition, FlowVision applies the dynamic mesh refinement by taking into account the motion of the heart-modeled surface, required by the CFD Euler model. The presented CFD approach to simulate the human internal blood flow is validated with data from MRI/MRT scans of the real heart and the respective simulation test cases are presented.
- Details
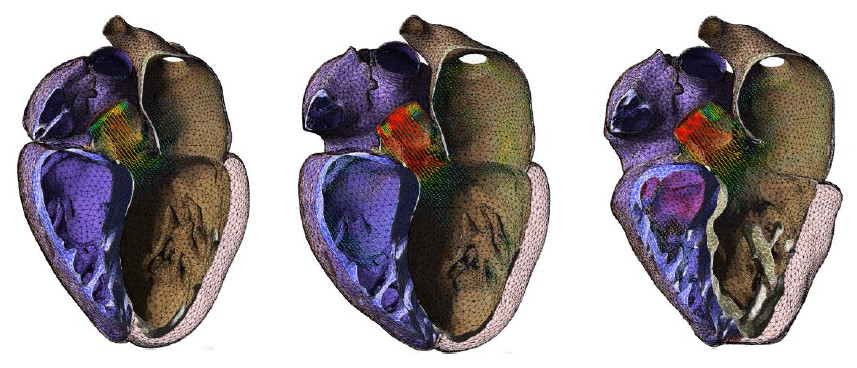
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in developed countries and continues to drive significant research aimed at improving diagnosis and treatment. In cases where therapeutic medical device intervention is warranted, it is important to account for device-heart interaction over both the short and long term. In the short term, cardiac motion can significantly impact device stability and performance (as in the case of artificial heart valves), while over the long term, modified blood flow patterns may lead to structural remodeling that can have adverse effects on cardiovascular function. Computational tools used for device design, sizing, and placement must therefore be able to account for cardiac/vascular tissue mechanics, blood flow, and the interaction between them. Moreover, such tools must allow for patient-specific modeling and provide interactive visualization capabilities that can support clinical decision-making and reduce operator error.
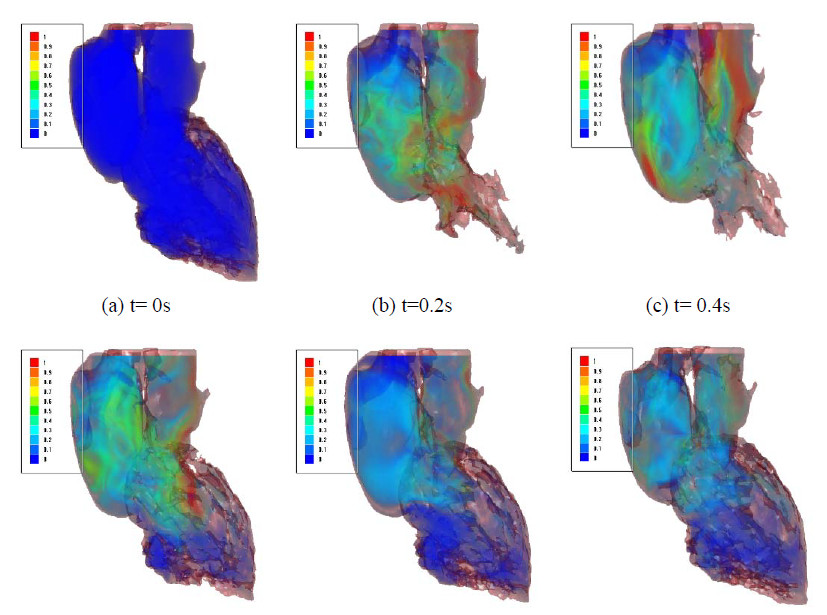
Blood flow velocity at different time points in the FSI simulation
In this paper, we describe a methodology for bidirectional fluid-structure interaction between the general purpose CFD code FlowVision and the SIMULIA Living Heart Human Model (LHHM), a dynamic, anatomically realistic, four-chamber heart model that considers the interplay and coupling of electrical and mechanical fields acting in concert to regulate the heart filling, ejection, and overall pump functions. The LHHM natively includes a 1D fluid network model capable of representing dynamic pressure/volume changes in the intra- and extra-cardiac circulation. In the current work, we first replace this network model with a full 3D blood model (solved in FlowVision) that provides detailed spatial and temporal resolution of cardiac hemodynamics driven by motions of the beating heart and constrained with appropriate time-varying boundary conditions derived from the literature. After validating this approach, we activate bidirectional coupling between the blood flow CFD model and the LHHM electromechanical model using the SIMULIA co-simulation engine and discuss modeling details and results of interest.
- Details
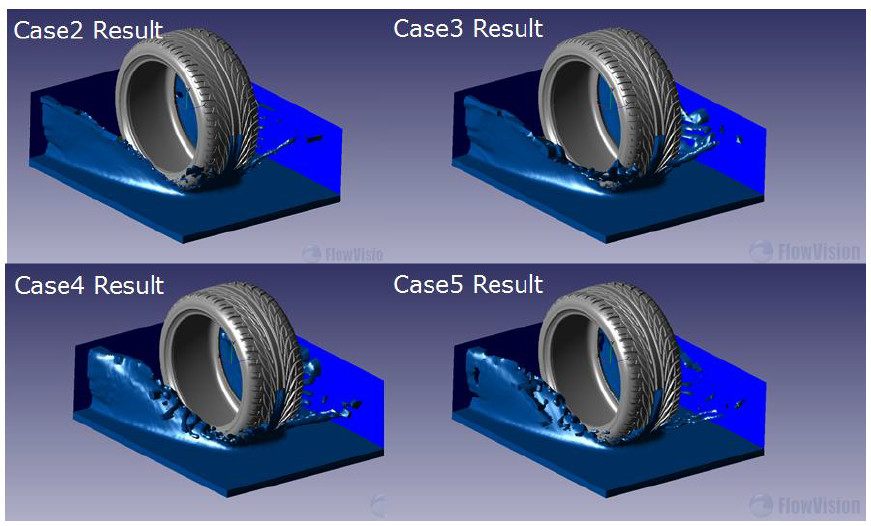
Hydroplaning is a major cause of wet-road accidents. The main contact element between the ground and vehicle is the tire. Tire safety and performance are therefore critically important. Wet roads present several uncontrollable factors. This paper uses CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) to analyze wet road hydroplaning effects. Fluid dynamics cannot be easily measured using normal experiments. Therefore the braking distance and record rolling vary by encoder. We propose another method to analysis it. By this result, the large groove and tire depth can reduce hydroplaning effects. A second method is modifying the tire void pattern which can reduce the hydroplaning extent by 29%.
- Details
The FDA (U.S. Food & Drug Administration) has partnered with academia and industry the Critical Path Initiative program to create a Guidance Document for industry-wide use proper validation and use of CFD models in the assessment of medical device safety.
CFD simulations are increasingly being used to determine flow patterns and fluid forces in order to evaluate blood-contacting medical devices. It is due to its potential to calculate the values of physical parameters that may affect the level of blood damage the device may cause, such as shear stress or dwell time. Although CFD can decrease the need for expensive prototyping and laboratory testing, there are no standardized and reliable methods available for using CFD techniques in this field.
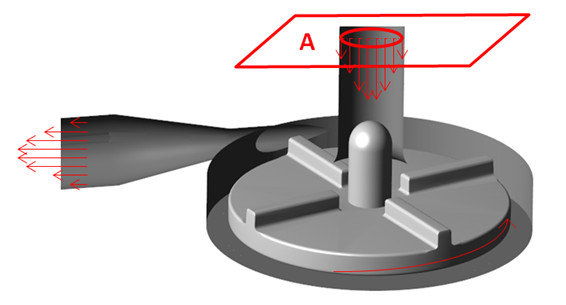
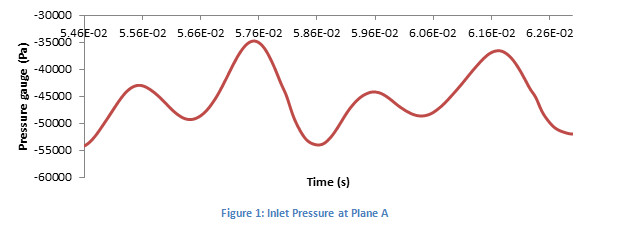
The purpose of this project is to determine the limits of the applicability of CFD techniques by comparing some parameters (such as gauge pressure or shear stresses) of the computational simulations of a blood pump in several working conditions against suitable experimental models. The different conditions included a wide range of velocity profiles at the inlet or different rotor velocities.
FlowVision moving body capability, together with the real CAD geometry import, has allowed the numerical simulation of this complex case with a relatively simple mesh. Time-dependent results during a whole revolution of the rotor have been obtained, providing consistent and more realistic data for the different scenarios. As example, variables as the pressure gauge behave cyclic with a period of a 1⁄4 of the revolution time, which is consistent with the number of blades.
- Details
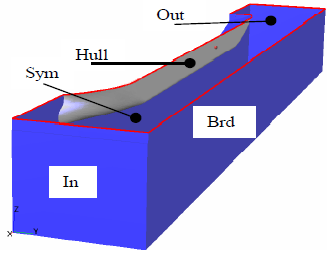
Nowadays, the Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) represents a standard design practice in solving the ship hydrodynamics problems, worldwide. In recent years CFD is actively in used by numerous maritime design organizations and related educational institutions. CFD is applied for propulsion research of the new-built or modernized ships, as it is well suited for the practice in the design and optimization of the ship hull form.
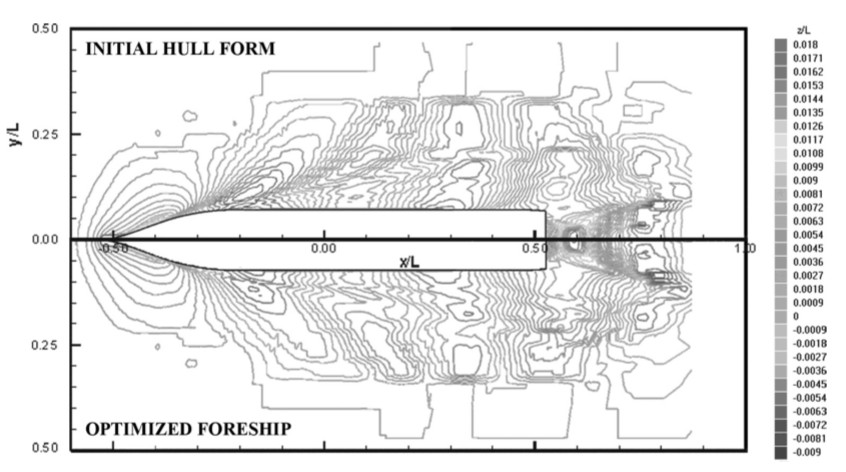
The presented results are also including the verification/validation analysis of the KCS hull form from the Gothenberg-2000 workshop has been developed by the authors of this paper, and through this comparative study, the best practices learned in this process, are shown. In this paper the FlowVision code is used as the CFD tool, integrating a new method of in-detail hull form design based on the wave-based optimization. The hull form design and its optimization are based on the systematic variation of the longitudinal distribution of the hull volume, while the vertical volume distribution is fixed or highly controlled. Such design process is underpinned with the respective data analysis of the obtained results, which are presented as the optimum distribution of the required hull volume. The final result is the optimized designed hull form, which shows interesting characteristics, as its resistance has decrease by 8.9% in respect to the well-known KCS hull form.
- Details
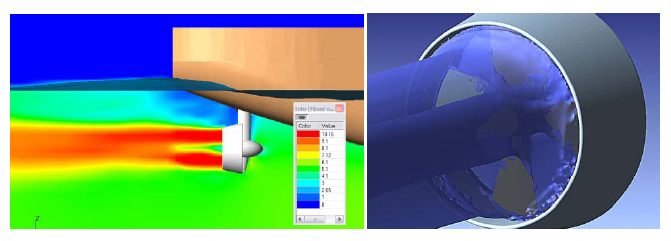
The constant grows of the motor fuel prices increases the requirements to the quality of ship propulsion study on the design stage. Some unusual approaches that applied during development of the "Volgo-Donmax" class ship project are described in this article.
- Details
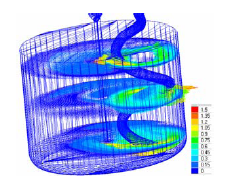
Mixing theory is important for its relevance in understanding some of the most fundamental problems involving bread dough flows, and for
its practical impact in connection with bakery industry and other food industries. Mixing is a crucial operation in the bakery industry. The bread dough is a very complex material, considered viscoelastic whose behavior depends on moisture content and temperature. The aim of this article is to develop advanced technology for modeling bread dough mixing, in order to provide a predictive capability of optimum design parameters of dough mixers using computational techniques.
- Details
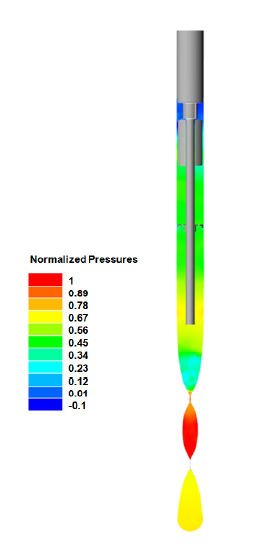
A deeper understanding of the interaction between machine, packaging material and liquid product during the forming process of pouches is enabled by the use of numerical simulation.
- Details
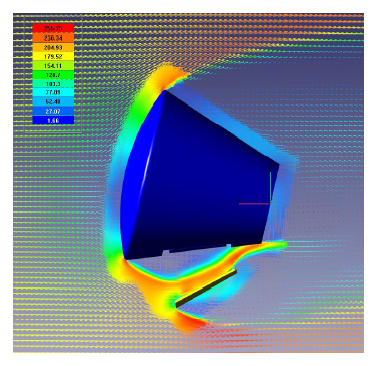
Two different complex problems arising during spacecraft design are discussed in this paper. One problem is a definition of impulse for a safety separation of a parachute container lid. Another problem is defining a shock-wave interaction on the spacecraft at turning on emergency rescue system. Both problem are very hard and expensive for solving by experimental methods, and RSC Energia gets here all benefits of numerical simulation by using CFD code FlowVision.
- Details
This paper outlines development of method for simulation of complex fluid flows having arbitrary motion of free surfaces. The method is based on rectangular grid with dynamic local grid adaptation. For approximation of a curvilinear computational domain boundaries and a free surface the subgrid geometry resolution method is used. The free surface tracking is provided by VOF method.
- Details
The aerodynamic performance and the bypass flow field of a vertical axis wind turbine under self-starting are investigated using CFD simulations in this paper.
- Details
The noise of domestic machines including lawnmowers becomes an urgent issue. As the technology matures, designers need better tools to predict performance and efficiency of these machines across a wide range of operating conditions and find optimal ways to reduce noise.